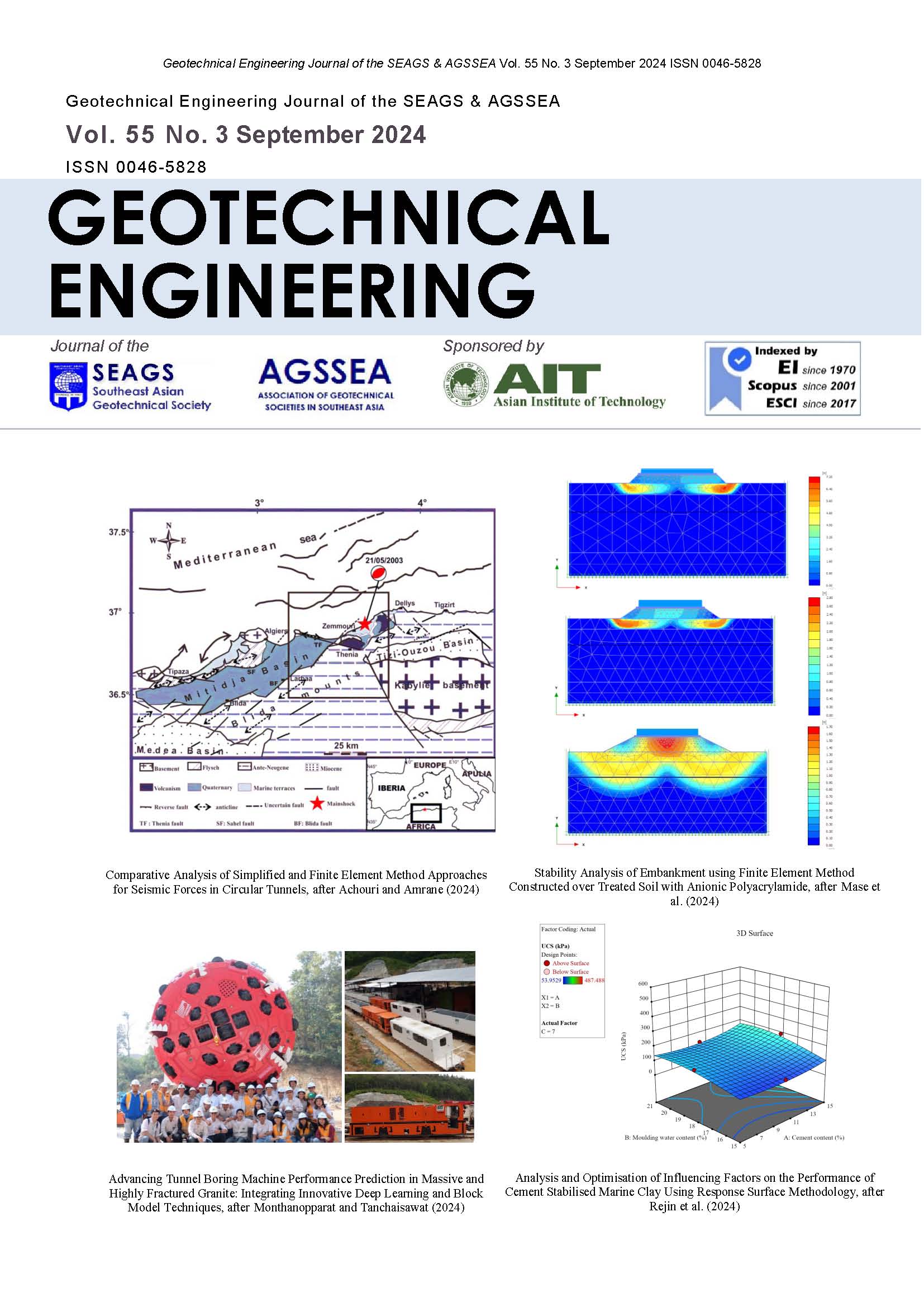
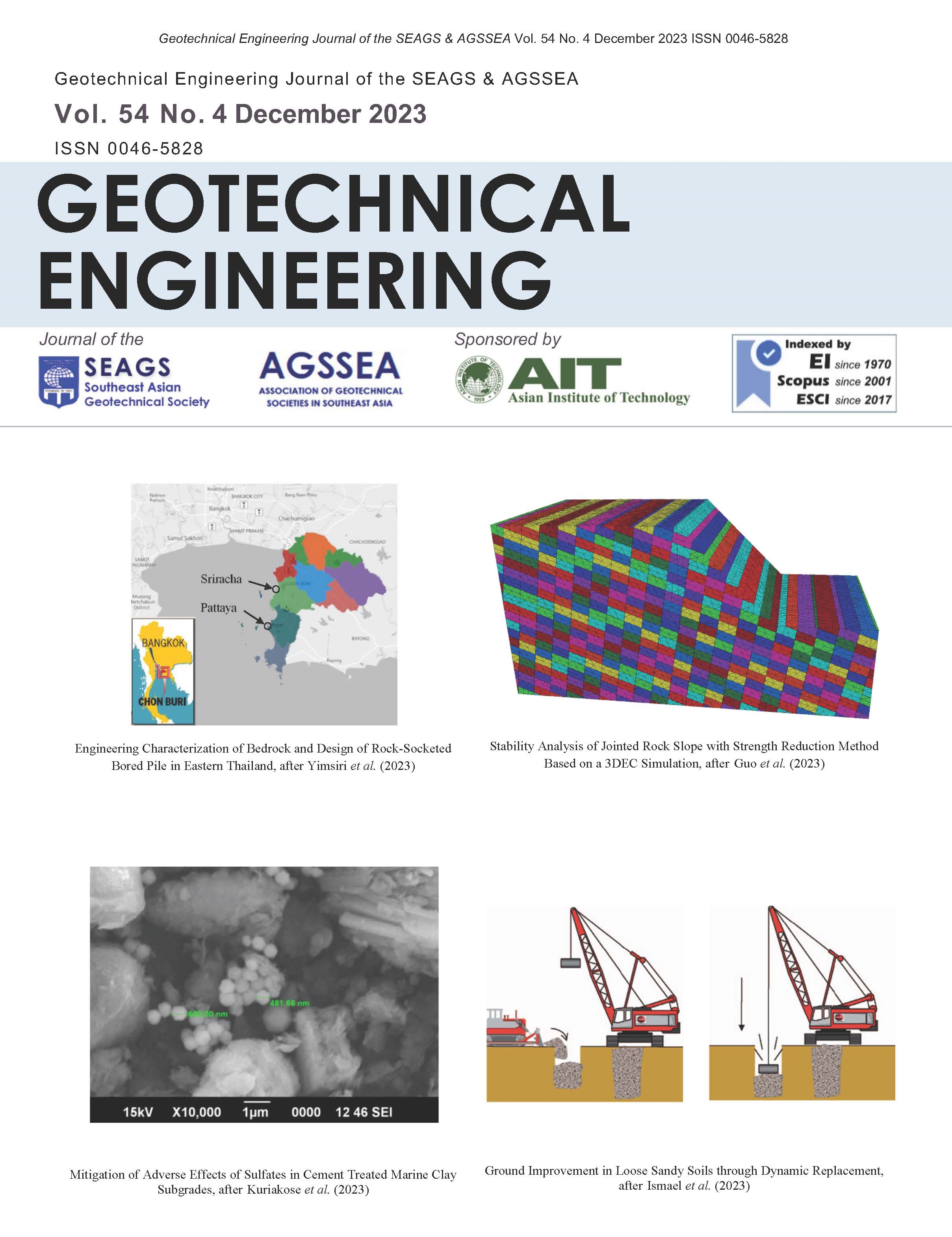
Modelling the Effects of Static Shear on the Undrained Cyclic Torsional Simple Shear Behaviour of Liquefiable Sand
By Gabriele Chiaro, L.I. Nalin De Silva and Junichi Koseki
ABSTRACT: Spanning from purely theoretical standpoint to practical applications, there is a particular interest to enhance understanding of the effects of static shear on the cyclic behavior of soil elements underneath sloped ground. To address this issue, two subsequent steps were undertaken in this study. First, a systematic laboratory investigation was carried out on Toyoura sand specimens subjected to various levels of combined static and cyclic shear stresses. Then, a new state-dependent cyclic model was developed. Since experimental findings have been exhaustively reported elsewhere, in this paper they are only briefly recalled for the benefit of comprehensiveness. Instead, the new model is presented in details and its performance is verified by simulating undrained cyclic torsional simple shear tests carried out on Toyoura sand specimens. Essentially, the model is built on an extended general stress-strain hyperbolic equation approach, in which the void ratio and stress level dependency upon non-linear stress-strain response of sand is incorporated. Besides, a novel empirical stress-dilatancy relationship is used to account for the effect of density on the stress ratio as well as to model the excess pore water pressure generation in undrained shear conditions as the mirror effect of volumetric change in drained shear conditions.
KEYWORDS: Constitutive soil model, Laboratory testing,Cyclic torsional simple shear, Static shear, Toyoura sand
Numerical Study on the Design of Reinforced Soil by Vertical Micropiles
By A. Kamura, J. Kim, T. M. Kazama, N. Hikita and S. Konishii
ABSTRACT: The mechanical behavior of the reinforced soil by vertically arranged micropiles was considered using the three-dimensional finite element analysis. To make effective use of space around the slope, soil needs to be reinforced using micropiles placed in a small area. The main objective of this investigation was to evaluate the mechanical influence of various micropile arrangements and to determine the effects of pile spacing for design purposes. Numerical simulations of three cases using different pile angles indicated the amount of slope displacement and the values of the sectional force of the micropiles differed significantly. Among the three cases, the maximum slope displacement was 1.7 times the minimum value. Finally, numerical simulations of three cases using different pile spacing was carried out to clarify the effects of pile spacing on the amount of slope displacement and the sectional force of the micropiles.
KEYWORDS: Reinforced soil, Vertical micropiles, Finite element analysis, Parametric study
Soil-water Coupled Analysis of Pore Water Pressure Dissipation in Performance Design – Examinations of Effectiveness in Reclaimed Ground
By Toshihiro Nonaka, Shotaro Yamada and Toshihiro Noda
ABSTRACT: Japan has a large number of reclaimed regions unimproved against liquefaction and countermeasures in such regions are necessary to prepare for a great earthquake. A new macro-element method has been proposed that involves applying the soil-water-coupledfinite deformation analysis code GEOASIA with an inertial term, and a numerical-analysis technique has been designed that quantitatively evaluates the improvement effect of the pore water pressure dissipation method (PWPDM). In this study, PWPDM effectiveness was examined for a reclaimed ground using the proposed method. Detailed examinations were conducted with the intention of developing a more advanced performance design, without being limited to the concept of the current design code. The main findings are as follows: 1) the proposed analysis code enables quantitative evaluation of the improved effectiveness of PWPDM in a reclaimed ground; 2) more advanced PWPDM designs are possible by not only suppressing the maximum excess pore water pressure to the permissible range of the current design code, but also evaluating the ground deformation adequately; and 3) the new macro-element method, capable of reproducing the phenomenon of well resistance, can evaluate the reduction in the improvement effect because of the degradation of drainage capability, thus making it useful for maintenance purposes such as drain clogging.
Keywords: Pore water pressure dissipation, Soil-water coupled analysis, Macro-element method, Reclaimed ground, Performance design
Comparison of Sheared Granular Soils: Same void ratio but Considerably Different Fabric
By Y. Fukumoto and S. Ohtsuka
ABSTRACT: This paper reports a comparison of two types of sheared granular soil specimens, with almost the same void ratios but considerably different fabric, using the discrete element method in two dimensions. The specimens are prepared by applying two different methods of particle generation; one specimen is generated by placing the particles geometrically, while the other specimen is generated by placing the particles randomly. Then, computational direct shear tests are conducted in order to compare the yielding behaviours of the two specimens. The obtained bulk shear responses show different trends, even though the values for the void ratio at the initial state are almost the same. Toward the critical state, however, the initial differences in the stress state and the granular fabric gradually disappear and eventually reach almost the same state. The results reveal that not only macroscopic quantities, but also the contact force distribution and the angular variation in contact forces, have a unique critical state. In particular, the angular distribution of contact angles inside the shear band is also found to have a unique critical state.
Keywords: Granular materials, Discrete element method, Shear behaviour
Coupled Analysis of Navier-Stokes and Darcy Flows by the Brinkman Equations
By S. Arimoto, K. Fujisawa and A. Murakami
ABSTRACT: Simultaneous analysis of see page flows in porous media and regular flows in fluid domains has a variety of applications to practical problems. The objective of this paper is to present a numerical method to simulate these two different flows simultaneously and continuously, and to investigate the influence of the Darcy flows in porous media on the Navier-Stokes flows in the fluid domain. To this end, the authors have employed the Darcy-Brinkman equations, which include the Navier-Stokes equations and can approximately describe Darcy flows by changing the values of porosity and hydraulic conductivity. The solutions of the Darcy-Brinkman equations are affected by two dimensionless quantity, i.e., the Reynolds number, Re and the Darcy number, Da. After the procedures to provide stable solutions of the governing equations are explained, this paper considers the two types of problems involving Navier-Stokes/Darcy coupled flows and the influence of the two dimensionless parameters on the solutions are investigated. One is the backward-facing step flow with a porous step, and the other is the preferential flows in porous media. The numerical results have shown that the permeability of the porous step slightly affects the reattachment of the flow in the former problem, and that the shape of the void or cavity in porous media changes the structure of the flow in it and the Darcy number changes the flux into the fluid domain in the latter problem.
KEYWORDS: Darcy’s law, Navier-Stokes equations, Coupled analysis, Darcy-Brinkman equations
Numerical Investigation on Mechanical Behaviour of Natural Barrier in Geological Repository of High-Level Radioactive Waste
By Y. Kurimoto, Y. L. Xiong, S. Kageyama and F. Zhang
ABSTRACT: It is commonly known that geological repository is regarded as the most practical way of permanent disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW). Yet, there are some engineering problems needed to be solved before its practical application. In geological repository, one of the most important factors is the thermo-hydraulic-mechanical (THM) behaviour of natural barrier. The aim of this paper is to investigate the influence of temperature on the deformation and the strength of host rocks, such as the soft sedimentary rock, with some element tests and the numerical simulations with a program of FEM named as SOFT based on a thermo-elasto-viscoplastic constitutive model.
Keywords: Soft sedimentary rock, Geological repository of HLW,Thermo-hydraulic-mechanical coupling
Change of Soil Properties in the Bengawan Solo River Embankment due to Drying–Wetting Cycles
By Trihanyndio Rendy Satrya, Ria Asih Aryani Soemitro, Toshifumi Mukunoki and Indarto
KEYWORDS: River embankment, Drying-wetting cycle, Compaction, In-situ investigation
Soft Ground Improvement at the Rampal Coal Based Power Plant Connecting Road Project in Bangladesh
By Sudipta Chakraborty, Ripon Hore, Fahim Ahmed and M. A. Ansary
KEYWORDS: Vertical sand drain, Soil improvement, Embankment, Road construction
Assessment on the effect of fine content and moisture content towards shear strength
By Badee Alshameri , Aziman Madun and Ismail Bakar
ABSTRACT: The shear strength τ, shear modulus G, friction angle ∅, and cohesion c are remarkable design parameters in the geotechnical and civil projects. These design parameters were affected by several factors. In this paper, the fine content and moisture content factors were evaluated. Numerous compacted sand-kaolin samples were test through the direct shear box test (by using shear rate equals to 1 mm/min, the samples dimension equals to 100 × 100 mm) to assess the effect of these factors. The results show interface between both effects of fine content and moisture content towards the shear strength parameters. According to the results; (1) there is no significant effect on shear strength parameters at low portions of fine content FC and moisture content w, (2) at higher portion of FC and w, bot FC and w show different relationships with shear strength parameters, (3) both relative high shear rate and low applied stress lead to present high value of friction angle (4) compact the soil mixtures with same compaction effort and different fine and moisture content lead to change the soil structure and void ratio thus produce regressive relationship between the friction angle toward density.
KEYWORDS: Fine content, Moisture content, Shear strength, Friction angle, Cohesion, Fines and water bond
Ground Response Based Preliminary Microzonation of Kathmandu Valley
By Dipendra Gautam, Hemchandra Chaulagain, Hugo Rodrigues and Hem Raj Shahi
ABSTRACT: This paper analyzes spatially selected 286 deep borehole logs reaching up to the bedrock and the results are presented in terms of amplification factor, ground acceleration and predominant period. The peak ground acceleration (PGA) is estimated to be 0.10 and 0.50 g indicating strong influence of nonlinearity in particular areas of Kathmandu valley wherein de-amplification is observed. The peak spectral acceleration is found to be varying from 0.30 to 1.75 g for the study area and soil predominant period is estimated in the range of 0.7 to 5 sec. Preliminary microzonation maps for PGA and soil predominant period are prepared and presented in this paper. Comparisons and interpretations on the basis of 1934 and 2015 earthquakes are presented in terms of damage scenario.
KEYWORDS: Hazard mapping, Nonlinear ground response analysis, Amplification factor, Peak ground acceleration, Soil predominant period; Kathmandu valley.
Investigation of the Use of Sugarcane Bagasse for Soil Reinforcement in Geotechnical Applications
By V. Oderah and D. Kalumba
ABSTRACT: The global initiative of minimizing the generation of waste materials and the reduction in the environmental footprints of industrial processes has impelled the innovation into their use in geotechnical applications. Use of these materials in this manner, especially as soil reinforcements, could help solve the drudgery and the secondary snags of disposing of the materials. This study therefore aimed at investigating the effects of sugarcane bagasse reinforcement on selected South African soils as well as the drawbacks of the environmental conditions on the composite formed. Different types of sugarcane bagasse were utilised in evaluating their effect on the shear strength characteristics of the composite. The results indicated a higher improvement in the angle of internal friction in finely grained soil compared to coarsely grained soil. Saturation of the composite in water insignificantly reduced the strength characteristics beyond 2 days. In addition, an increase in the shear characteristics depended on the bagasse type and content, and on the vertical load.
KEYWORDS: Sugarcane bagasse, Shear strength, Industrial waste material, Fibre reinforcement, Saturation
Quasi-Static Numerical Modelling of an ore Carrier Hold
By S. Daoud, I. Said, S. Ennour and M. Bouassida
ABSTRACT: The problems associated with ore carriers’ incidents, have preoccupied international organizations and many research laboratories which have been mobilised to identify the causes and seek for the solutions. The cargo liquefaction is considered to be the major cause of ore carriers’ capsizing. The final aim of this research is to establish a new test procedure for evaluating the shear strength of loaded ore in view of its liquefaction prevention. First, a brief review is presented about the possible origins of cargo instability and examines the stress distribution by means of a quasi-static numerical modelling. Second, an assessment of the shear ratio variation, in terms of the hold inclination is established. According to this analysis, at a 15° hold inclination, the maximum shear ratio is less than 0.2 in all pile areas except under the residual slopes and at the surface that are assumed to be the most vulnerable parts.
KEYWORDS: Cargo, Ore carrier, Liquefaction, Numerical modeling, Shear ratio.
Shear Strength of an Expansive Overconsolidated Clay Treated with Hydraulic Binders
By A. Mahamedi and M. Khemissa
ABSTRACT: This paper presents and analyzes the results of a series of identification; compaction and direct shear tests performed in accordance with the Algerian standards on expansive overconsolidated clay treated with locally manufactured hydraulic binders (composed Portland cement and extinct lime). This clay comes from the urban site of Sidi-Hadjrès city (wilaya of M’sila, Algeria), where significant damages frequently appear in the road infrastructures, roadway systems and various networks and in civil and industrial light structures. Tests results show that the geotechnical parameters deduced from these tests are concordant and confirm the shear strength improvement of this natural clay treated with cement or lime and compacted under the optimum Proctor conditions. However, contrary to its mineralogical characteristics which do not seem to be affected by the treatment, this expansive natural clay is characterized by as well drained as undrained shear strength sensitive to stabilizer content; the best performances are obtained for a treatment corresponding to 8% cement or lime content.
KEYWORDS: Expansive clay, Treatment, Hydraulic binders, Shear strength.
Simplified Method for Designing Piled Raft Foundation in Sandy Soils
By N. M. Alsanabani, T. O. AL-Refeai and A. O. Alshenawy
ABSTRACT: The main purpose of this study is to develop a simplified method for computing the load carried by piles, and settlement of piled raft based on the characteristics of an un-piled raft, pile group, and soil. These are important criteria for preliminary piled raft design. Based on the results obtained from finite element analysis, simplified formulas and curves are generated for different conditions of sand and different pile spacing. These formulae and curves contain the stiffness ratio and efficiency factor of the un-piled raft and pile groups. The results of the proposed method were validated using the Poulos–Davis–Randolph method.
KEYWORDS: Stiffness, Raft, Piles, Load sharing, Settlement.
Experimental Study on the Durability of Soil-Cement Columns in Coastal Areas
By Pham Van Ngoc, Brett Turner, Jinsong Huang and Richard Kelly
ABSTRACT: Deep soil mixing is one of the most commonly used ground improvement techniques. With high sulphate content in soil and seawater, stabilised soil in coastal areas can deteriorate due to sulphate attack. In this research, the degradation in strength of cement treated soil exposed to synthetic seawater is measured by uniaxial compression and needle penetration testing. Three exposure conditions, namely 100% seawater, 200% seawater and sealed condition (control samples), were used to measure the deterioration level due to the effect of sulphate. In addition, the extent of the portlandite consumption was also measured by Thermogravimetric Analysis which reflects the calcium distribution in the soil-cement columns. The test results show that the deterioration occurs deeper and faster in higher seawater environments. Furthermore, in contact with increasing sulphate concentration, the deterioration shows a close relation with calcium distribution.
KEYWORDS: Soil-cement column, Deterioration, Needle penetration test, Sulphate concentrations, Deterioration depth.
The Change Laws of Strength and Selection of Cement-sand Ratio of Cemented Backfill
By Xiaoming Wei, Changhong Li, Xiaolong Zhou, Baowen Hu, Wanling Li
ABSTRACT: Lilou Iron Mine is the largest domestic underground backfill mining and uses advanced whole tailings cemented filling process system. For the backfill, both the change law of strength development and the cement-sand ratio are important considerations for design. A differentiation analysis was performed of the strength of laboratory test blocks at the age of 28d and in situ cemented backfill samples. When the filling slurry concentration was 72% and cement-sand ratio was 1:4, the in situ coring strength was 2.98 MPa higher than that of laboratory-cured specimens; when the slurry concentration was 68% and cement-sand ratios were 1:4, 1:6 and 1:8, the in situ coring strength was 1.68MPa, 2.33 MPa and 1.44 MPa higher than that of laboratory-cured specimens. With an increase of filling height, the change laws has been explored of downward parabola in conditions that the strength difference is consistent with the bulk density difference of the cemented backfill. The stress of cemented backfill with different ratios were calculated and analyzed on the basis of ANSYS numerical simulation and similar filling mines. According to the position of stress concentration and change law of strength difference, this paper proposes an design scheme for high-stage cemented backfill with ratio parameters at different heights.
KEYWORDS: High-stage cemented backfill, Strength difference, Bulk density, Ratio desig
Numerical Modelling of Ground Subsidence at an Underground Coal Gasification Site
By T.C. Ekneligoda, L.T. Yang, D. Wanatowski, A.M. Marshall, and L.R. Stace
ABSTRACT: A detailed numerical modelling study was carried out to represent geotechnical aspects of the Wieczorek underground coal gasification (UCG) site in Poland. A coupled thermos-mechanical numerical model was created to represent a single coal burning panel. The coal burning process was simulated by modifying the energy balance equation with an additional term related to the calorific value of coal as a source. Temperature dependent material properties were assigned to the coupled thermal-mechanical model according to published data. In the model, the burning zone spread about 7.5m laterally after 20 days of burning. Results from the coupled model were used to gauge a worst-case scenario in terms of the potential size of a formed cavity. This data was used within a less computationally expensive mechanicalonly numerical model in order to evaluate the ground subsidence caused by the worst-case scenario for single and multiple UCG burning panels. The single panel burning resulted in 23mm of ground subsidence at the top of the model after long term coal burning. The ground subsidence measured at the top of the model, at the center point of the gasification arrangement, was approximately 72mm when five panels were burnt with an edge to edge panel distance of 5m; this was increased to 85mm for seven panels. The numerical modelling results have implications to the industrial application of UCG.
KEYWORDS: Numerical model, Underground coal gasification, Calorific value, Subsidence.