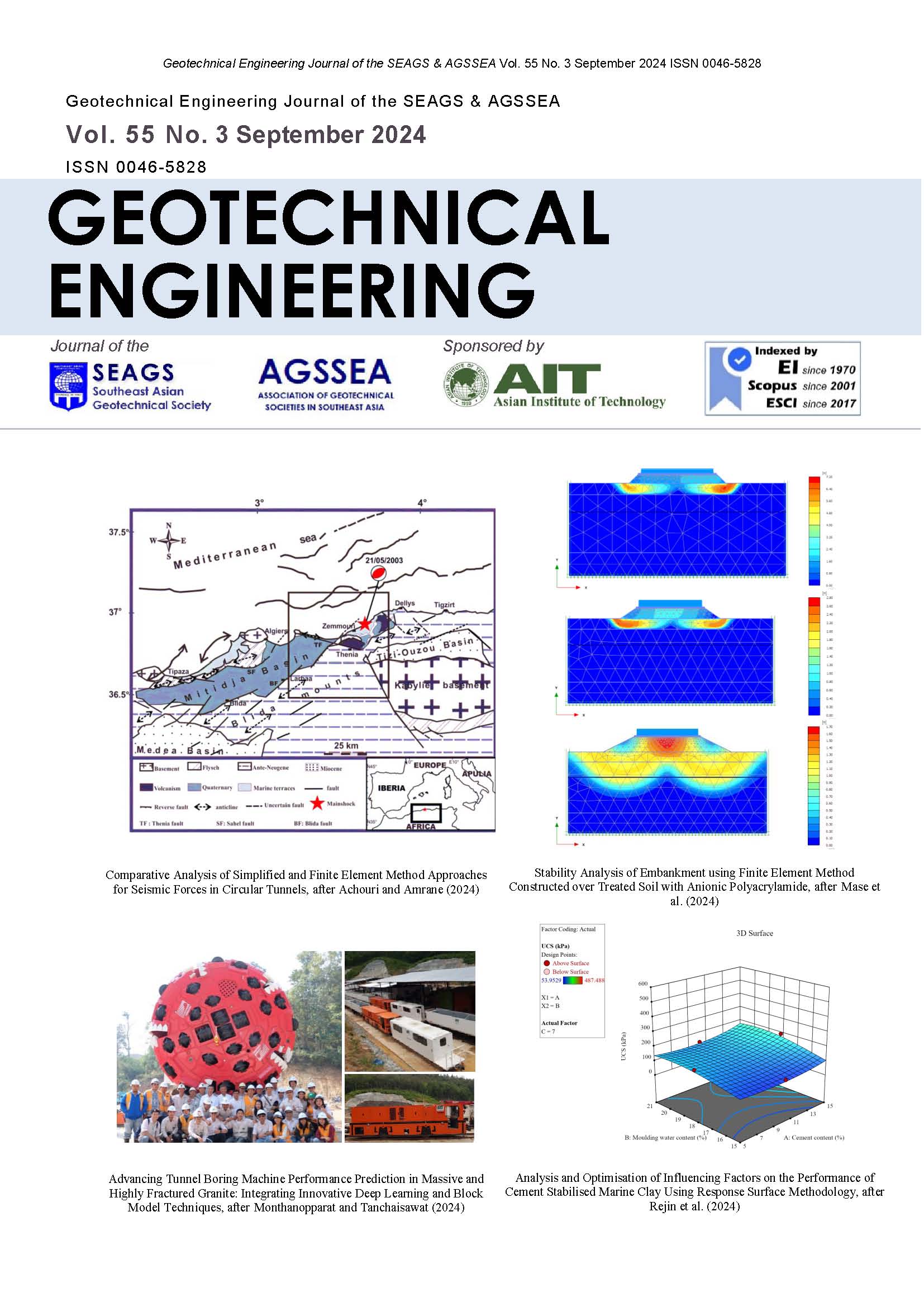
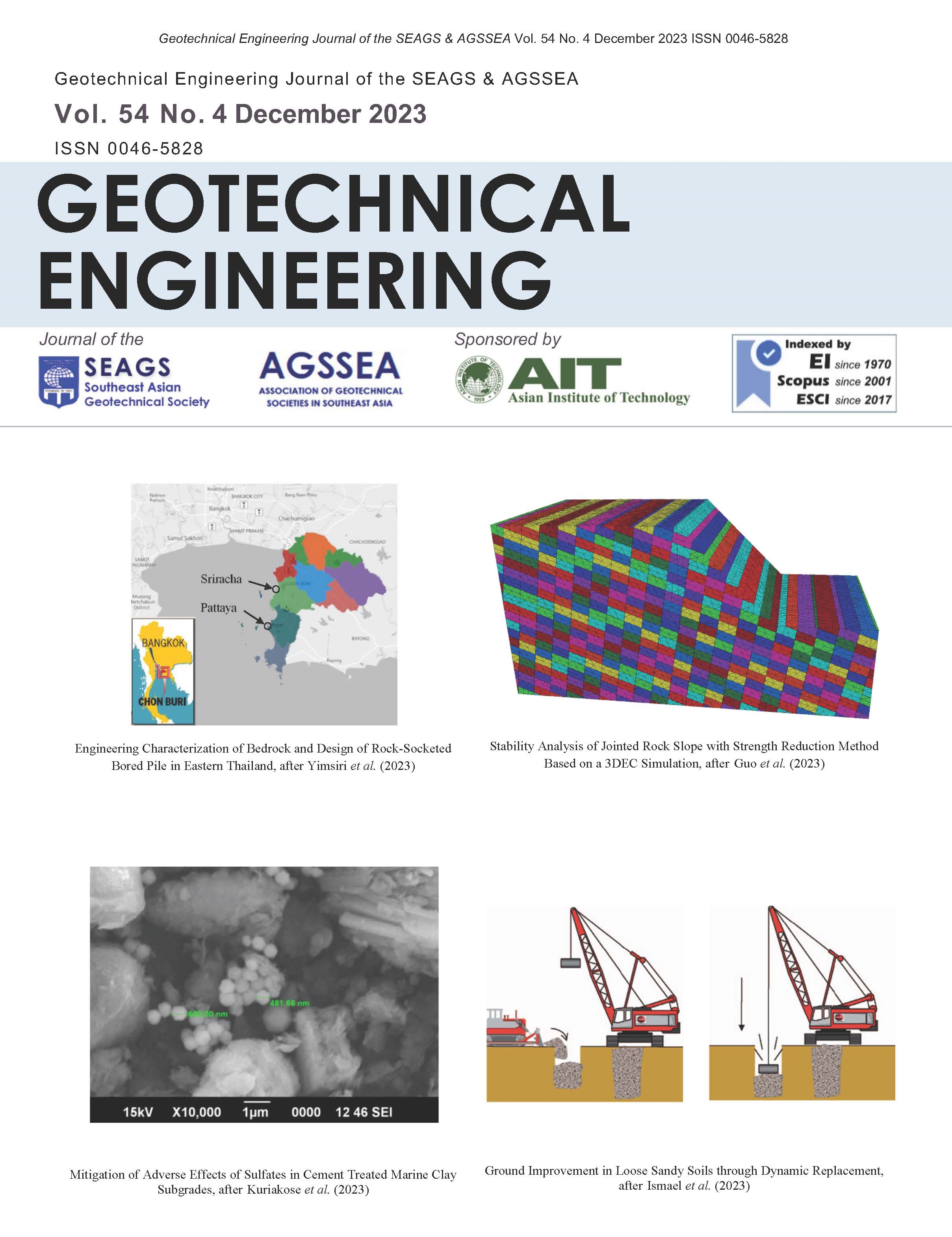
Behaviour of Clay Subjecting to Vacuum and Surcharge Loading in an Oedometer
J.-C. Chai, J. P. Carter, A. Saito and T. Hino
ABSTRACT: The deformation of clayey soil subjected to the combination of a vacuum pressure and a surcharge load in an oedometer apparatus, with either vertical or inward radial drainage, has been investigated experimentally. A parameter Kw, defined as the horizontal effective stress exerted on the wall of the consolidation ring (s’hw) divided by the vertical effective stress (s’v) in the soil specimen is suggested as an indicator of the tendency for lateral deformation under field conditions. It is observed that if the value of Kw is close to the value of K0 of the soil (the ‘at-rest’ earth pressure coefficient), there should be very limited lateral displacement in field situations. The laboratory test results show that during the loading process, the value of Kw is mainly influenced by the ratio of the magnitude of the surcharge pressure to the vacuum pressure (RL) and the rate of surcharge loading (SLR). At the end of consolidation the value of Kw increases with increasing RL, but it is almost independent of SLR for the conditions investigated. In the presence of a vacuum pressure, at the end of consolidation the value of Kw is usually less than the original value of K0 of the soil. The test results also indicate that Kw has a strong correlation with the synthetic non-dimensional loading parameter, RLS, as defined by Chai et al. (2013), which includes the effects of both RL and SLR as well as the consolidation properties of the soil. It is suggested that the parameter RLS can be used to predict lateral displacements under field conditions that involve combined surcharge and vacuum pressure loading.
KEYWORDS: Vacuum consolidation, combined loading, oedometer, earth pressure, deformation
Behaviour of Geogrid Reinforced Abutments on Soft Soil
Ennio M. Palmeira, André R.S. Fahel and Gregório. L. S. Araújo
ABSTRACT: The behaviour of embankments on soft soils is a complex problem, particularly when the substitution of the soft material is not cost effective. In this case, the use of geosynthetics may be a feasible and economical solution for the stabilization of the embankment and reduction of the effects of differential settlements. This paper shows an investigation on the use of geogrid reinforcement in combination with pre-fabricated vertical drains (PVD) to accelerate soft soil consolidation in abutments for the duplication of the BR-101 highway, in Brazil. The instrumentation of bridge abutments included inclinometers, settlement and horizontal displacement plates, full-profile settlement gauges and piezometers, as well as strain gauges in the reinforcement layer. The results obtained showed that one of the abutments almost collapsed due to wrong construction practice and reinforcement specification. Insufficient reinforcement tensile force mobilization along the embankment transverse direction combined with wrong reinforcement orientation yielded to large embankment displacements and the initiation of failure. This failure mechanism could have been predicted with the use of current slope stability analysis for this type of problem. The results also showed the beneficial effect of the reinforcement for the stability of the embankment and reduction of lateral displacements of the abutments.
KEYWORDS: Reinforced abutments, soft soil, geogrid, stability, strains
Geocell-Reinforced Granular Fill under Static and Cyclic Loading: A Synthesis of Analysis
X. Yang and J. Han
ABSTRACT: Geocell is a three-dimensional geosynthetic that provides direct lateral confinement to the infill material. In recent years, the use of geocell-reinforced granular fill as a load supporting layer has received increased attention. In the past, lack of well-developed design methods that could quantify the benefit of geocell reinforcement limited the application. To fill the gap between the design and the application, fundamental, theoretical, and applied research projects have been carried out in several research institutes. This paper presents a synthesis of these studies on the analysis of geocell-reinforced granular fill. Due to the differences of soil behaviour under static and cyclic loading, theoretical and numerical analyses are summarized in this paper based on loading conditions. Experiments performed to facilitate the theoretical and numerical analyses are also reviewed. Recommendations are made for areas of future research.
KEYWORDS: Geocell, geosynthetic reinforcement, granular fill, static load, and dynamic load
Electrical Vertical Drains in Geotechnical Engineering Applications
J. K. Lee and J.Q. Shang
ABSTRACT: Electrical vertical drains (EVDs) have been applied for improvement of soft clays. In this state of the art review, an overview of the theory of electrokinetics is presented, followed by discussions of the characteristics and limitations of some EVDs via laboratory and field experimental studies on electrokinetic stabilization of geo-materials. The predominant mechanism of electrokinetic stabilization includes electroosmosis, the movement of pore water in soil driven by a direct current (DC), and electro cementation induced by electrochemical reactions at electrodes. The overall effect of electrokinetic treatment is the increase in the soil shear strength and decrease in the soil compressibility. The technique has been applied successfully in geotechnical engineering, while one of the challenges is corrosion of anodes that are typically made of steel or copper. More recently, conductive polymer products have been developed, such as electrokinetic geosynthetics (EKGs) and electrical vertical drains (EVDs). This paper presents case histories on using EVDs in soil improvement. The authors hope that this review serves as a guidance for future research and development of electrokinetic treatment of geo-materials using EVDs.
KEYWORDS: Electrokinetics, electrical vertical drains (EVDs), physiochemical properties, soil shear strength, and settlement
Design and Performance of Soft Ground Improvement Using PVD with and without Vacuum Consolidation
P.V. Long, D.T. Bergado, L.V. Nguyen and A.S. Balasubramaniam
ABSTRACT: This paper presents the soft ground improvement using Prefabricated Vertical Drains (PVD) including PVD installation and preloading techniques, settlement and stability design calculations, observational methods and back analyses of monitoring data and performance of conventional preloading with surcharge fill and preloading using vacuum consolidation method (VCM) in combination with fill embankment. Several case histories were studied. The monitored data illustrated that the effectiveness of VCM is dependent on the method of applying vacuum pressure to the PVDs. Measured pore pressure in the PVDs at different depths indicated that the effective vacuum pressure inside the PVDs is distributed uniformly along the PVD depth with a magnitude of over 80 kPa for VCM using airtight membrane. Back-calculated ch values from measured settlement data using Asaoka method confirmed that with the assumed values of ds/dm = 2 and kh/ks = 2, the corresponding value of ch/cv,oed = 3 to 5 were obtained for both soft Bangkok (BKK) clay and soft clays in Mekong River Delta (MRD). Also, the linear relationship between compression index and water content for soft clays in MRD is similar to that of BKK clay. The settlements versus time calculated by 1-D method are in very good comparison with measured data for both conventional preloading and VCM considering the vacuum pressure as an induced vertical stress distributed uniformly in the PVD zone. From the results presented in this paper, simple procedures can be made for selection of soil parameters and design calculations of embankments on PVD improved soft ground using conventional preloading and vacuum consolidation.
KEYWORDS: Settlement, stability, soft clay, ground improvement, PVD
Reassessment of Long-Term Performance of Geogrids by Considering Mutual Interaction among Reduction Factors
Han-Yong Jeon and Yuan Chun Jin
ABSTRACT: For estimating allowable tensile strength of geogrids by reduction factor, it has a limit not to consider interaction force among reduction factors. Junction strength would be reduced by installation damages or chemical degradation as same as tensile strength. Single junction test method cannot properly cover for damaged samples and shows large deviations as it does not consider scale effect. Especially for calculating shear strength, no reasonable study to consider all reduction factors was conducted yet. Therefore, in this study, (a) reduction factors that may affect the long-term performance of geogrids were revaluated to consider various application conditions and (b) accurate long-term allowable tensile strength was calculated to consider interrelation among reduction factors. Creep results after installation damage and chemical resistance test showed lower value than that of GRI GG-4 calculation. After installation damage and chemical resistance test, the reduction factor of junction strength was less than that of tensile strength. Finally, shear strength before and after installation damage showed no change before and after installation.
KEYWORDS: reduction factor, junction strength, scale effect, long-term performance, GRI GG-4
Simulations of PVD Improved Reconstituted Specimens with Surcharge, Vacuum and Heat Preloading using Axisymmetric and Equivalent Vertical Flow Conditions
P. Voottipruex and D.T. Bergado, and W. Wongprasan
ABSTRACT: This paper presents the simulations of prefabricated vertical drain (PVD) improved reconstituted specimens with surcharge preloading (PVD), vacuum and surcharge with PVD (Vacuum-PVD), heat and surcharge with PVD (Thermo-PVD), heat plus vacuum and surcharge with PVD (Thermo-Vacuum-PVD) from large scale consolidometer tests in the laboratory. The flow conditions included axisymmetric conditions with horizontal (Kh) and vertical (Kv) permeabilities as well as equivalent vertical permeability (Kev) using backcalculated coefficient of horizontal consolidation (Ch). The simulation results indicated that the settlements and excess pore pressures obtained from axi-symmetric and equivalent vertical flows were similar at the same ratio of horizontal permeability at undisturbed zone to horizontal permeability at smear zone (Kh/Ks). The back-calculated Ch values were 1.93, 2.23, 4.17 and 4.38 m2/yr as well as the corresponding Kh/Ks values were 3, 2.7, 1.4, and 1.1, for PVD, Vacuum-PVD, Thermo-PVD and Thermo-Vacuum PVD, respectively. The Ch values increased while the Kh/Ks values decreased corresponding to PVD, Vacuum-PVD, Thermo-PVD, and Thermo-Vacuum PVD, respectively.
KEYWORDS: Prefabricated vertical drains (PVDs), equivalent vertical permeability (Kev), heat and surcharge preloading, numerical simulation
Reinforced Embankments on Soft Deposits: Behaviour, Analysis and Design
C. Taechakumthorn and R.K. Rowe
ABSTRACT: This paper reviews the key mechanisms on how basal reinforcement improves embankment behaviour through an examination of cases where embankments were constructed on soft organic clay and peat. The embankment responses from undrained and partially-drained simulations are compared to highlight the effect of consolidation during the construction. The benefits from the combined use of basal reinforcement and PVDs are presented. This paper also provides an overview of a design approach for embankments on soft ground taking account the interaction between basal reinforcement and PVDs as well as explores the effect the time-dependent behaviour of geosynthetics and rate-sensitive soils on the long-term performances of reinforced embankment under working condition. The limitations of the current design method are discussed. Finally a case study involving a reinforced embankment constructed over soft sensitive clay with a weathered crust is presented to illustrate the effect a stiff crust and soil structure can have on the effectiveness of the basal reinforcement used for this particular case.
KEYWORDS: Reinforced embankment, soft soil, basal reinforcement, geotextiles, geogrids
Current State of the Art in Vacuum Preloading for Stabilising Soft Soil
C. Rujikiatkamjorn and B. Indraratna
ABSTRACT: In this paper the analytical solutions for radial consolidation that include time dependent surcharge loading and vacuum pressure are proposed, whilst also considering the impact of the parabolic variation of permeability in the smear zone. The use of the spectral method for multilayered soil consolidation is introduced and verified. The Elliptical Cavity Expansion Theory is used to predict the extent of soil disturbance (smear zone) caused by the installation of mandrel driven vertical drains. The predicted smear zone is then compared to the data obtained from large-scale radial consolidation tests. Furthermore, the advantages and limitations of applying a vacuum through vertical drains are discussed using the proposed solutions. The vacuum pressure applied generates a negative pore water pressure that increases the effective stress within the soil, which leads to an accelerated consolidation. Vacuum pressure is modelled as a distributed negative pressure (suction) along the length of the drain and across the surface of the soil. Analytical and numerical analyses that incorporate the Authors’ equivalent plane strain solution are conducted to predict the excess pore pressures, lateral and vertical displacement. The application of the theoretical models for selected case histories at the site of the 2nd Bangkok International Airport and the Port of Brisbane, are discussed and analysed. The predictions are compared with the available field data and show that the proposed model can be confidently used to predict the performance with acceptable accuracy through rigorous mathematical modelling and numerical analysis. The research findings verify that the role of the smear zone and vacuum distribution can significantly affect the consolidation of soil, but these aspects need to be modelled appropriately to obtain reliable.
KEYWORDS: Analytical modelling; case history; numerical modelling; vacuum consolidation; vertical drain
Jet Grouting Practice: an Overview
Z.F. Wang, S.L. Shen, C.E. Ho and Y.H. Kim
ABSTRACT: Jet grouting is one of the most popular ground improvement techniques due to its applicability in almost all soil types. In this overview, the historical progress of technology development in jet grouting is briefly described, followed by the trace of the development of empirical and theoretical approaches for predicting the achievable diameter of a jet grout column. This paper also introduces a recently developed jet grouting technique called the Twin-Jet method. Twin-Jet method was developed to achieve quick solidification of soft soils by jetting with two types of binders, cement-slurry and sodium silicate (water glass) as an accelerator. This technique is particularly advantageous in horizontal jet grouting applications. Two case histories are presented to demonstrate the performance of Rodin Jet Pile (RJP) method in the soft clayey and sandy soils in Shanghai and the application of the Twin-jet method in sandy soils in South Korea.
KEYWORDS: Soft deposit, Jet Grouting, Diameter, Twin-Jet, Two binders
Deep Mixing Method in Japan
Masaki Kitazume
ABSTRACT: The Deep Mixing Method (DMM), a deep in-situ soil stabilization technique using cement and/or lime as a stabilizing agent, was developed in Japan and in the Nordic countries independently in 1970s. Due to its wide applicability and high improvement effect, the method has gained increased popularity in many countries. The method has been successfully employed in thousands of projects and the volume of improved soil from 1977 to 2010 exceeded 100 million cubic meters in the Japanese market alone. In the past three to four decades, traditional mechanical mixing has been improved to meet changing needs. Also new types of technologies have been introduced in the last 20 years and put into practice; e.g. high pressure injection and hybrid of mechanical and high pressure injection. The design procedures for various infrastructures were standardized by responsible organizations in Japan and revised several times. The manuscript presents a State of the Art on the Deep Mixing methods in Japan that covers the machinery, design, construction and quality control and assurance of the Deep Mixing Method.
KEYWORDS: Ground Improvement, Deep Mixing Method, Design, Execution, Quality control and quality assurance
Recent Studies of Geosynthetic Tubes and Mattress: an overview
Wei Guo, Jian Chu and Shuwang Yan
ABSTRACT: Geosynthetic tubes have been used in recent years in many projects related to coastal protection, dike construction, flood control and waste sludge dewatering purposes. The geosynthetic mattress method that uses flat mattress like geosynthetic containers have also been developed and used in several projects. The applications of geosynthetic tubes and geosynthetic mattresses are summarized in this paper. The existing analytical methods for different kinds of geosynthetic tubes are also summarized and critically reviewed in this paper. Methods for experimental studies and numerical analysis of geosynthetic tubes and mattresses are also reviewed and discussed.
KEYWORDS: Geotextile tube, geosynthetic tube, geosynthetic mattress
Design Method for Bearing Reinforcement Earth Wall
S. Horpibulsuk, C. Suksiripattanapong and A. Chinkulkijniwat
ABSTRACT: The bearing reinforcement was developed as a cost-effective earth reinforcement. It is composed of a longitudinal member and transverse members. The longitudinal member is made of a deformed bar, which exhibits a high pullout friction resistance. The transverse members are a set of equal angles, which provide high pullout bearing resistance. The bearing reinforcement earth (BRE) walls have been applied as a bridge abutment and a retaining structure along mountainous areas in several projects of the Department of Highways, Thailand since 2008. Based on the laboratory and field studies and design experience, the design method of the BRE wall is presented. The examination of external stability is performed using the conventional method (limit equilibrium analysis) assuming that the composite backfill-reinforcement mass behaves as a rigid body. The internal stability deals with rupture and pullout resistances of the reinforcement. The pullout resistance of the bearing reinforcement is approximated using the modified punching shear mechanism. The maximum tension plane is the bilinear failure mechanism (coherent gravity structure hypothesis). Finally, a design procedure, which commonly used in Thailand, is summarized and suggested.
KEYWORDS: bearing reinforcement, inextensible reinforcement, mechanically stabilized earth wall, design method
Current State of Knowledge on Thermal Consolidation using Prefabricated Vertical Drains
H. M. Abuel-Naga, G. A. Lorenzo and D. T. Bergado
ABSTRACT: Several research works have demonstrated that subjecting normally consolidated clays to temperature less than the boiling point of water (100oC) will have positive effects on its hydro-mechanical behaviour. Such effects can be exploited in improving the performance of the well-known preloading ground improvement technique that utilizes prefabricated vertical drains (PVDs). In this review paper, the applicability of a novel prefabricated vertical thermal drain (PVTD) will be presented and discussed using results of large oedometer tests and full-scale embankment tests on soft Bangkok clay. The large oedometer test results gave promising outcomes since the temperature accelerates the rate of consolidation and increases the amount of total settlement. The viability of the proposed technique was also confirmed by the full-scale embankment test results. The success of the proposed technique can be attributed to the thermally induced volume change and the increase in the hydraulic conductivity as the soil temperature increases.
KEYWORDS: Thermal consolidation, temperature effects, Bangkok clay, prefabricated vertical drain (PVD), ground improvement